Safeguarding Heavy-Duty Operations: The Importance of Bolt Tensioning
Bolt tensioning and torquing are two common methods for securing joints in heavy-duty applications, each with its own set of advantages and drawbacks. In this guide, we'll explore the differences between bolt tensioning and torquing, the importance of tensioning in heavy-duty industries like oil & gas, and the benefits of using Hydraulic Tensioners, particularly in turbomachinery applications.
1. Understanding Bolt Tensioning and Torquing
Bolt tensioning involves applying a load to a bolt to create tension, measured in pounds-ft, whereas torquing involves using a wrench to tighten the bolt, measured in Nm or ft-lbs.
Torquing relies on friction between the bolt and the surfaces it contacts, leading to potential inaccuracies and difficulties, especially in tight spaces.
Bolt tensioning eliminates many variables present in torquing, providing improved accuracy and repeatability, particularly in applications where precise clamping force is critical.
2. Importance of Tensioning in Heavy-Duty Applications
In industries like oil & gas, proper bolt tensioning is crucial for ensuring equipment integrity, safety, and operational efficiency. Achieving and maintaining accurate and uniform bolt tension is vital to prevent leaks, maintain structural integrity, and avoid costly downtime.
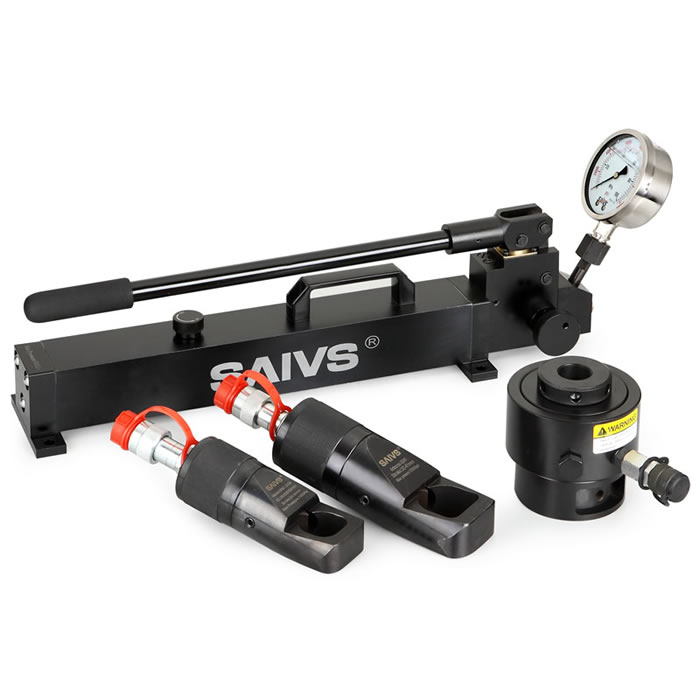
3. Advantages of Hydraulic Tensioners
Hydraulic tensioners have emerged as the preferred choice for heavy-duty bolt tensioning in industries like oil & gas, offering several advantages:
High Precision and Accuracy: Hydraulic tensioners provide precise and consistent bolt tensioning, ensuring accurate and uniform tension across multiple bolts.
Increased Efficiency: Hydraulic tensioners reduce the time and effort required for tensioning bolts, improving productivity and reducing downtime.
Uniform Tensioning: They apply force uniformly across the bolt, minimizing the risk of uneven tension distribution and enhancing structural integrity.
Safety: Hydraulic tensioners offer enhanced safety features, including overload protection and controlled release mechanisms, reducing the risk of accidents or equipment damage.
Versatility and Ease of Use: They are adaptable to various bolt sizes and configurations, lightweight, compact, and require minimal manual effort.
Reliability and Durability: Built to withstand demanding conditions, hydraulic tensioners ensure long-term reliability and durability in heavy-duty applications.
4. Advantages of Hydraulic Tensioners in Turbomachinery Applications
Hydraulic tensioners offer specific advantages in turbomachinery applications, including:
Tight Spaces: They can fit into restricted spaces where traditional tools may not access, ensuring proper loading.
Repeatability & Precision: Hydraulic tensioning reduces uncertainties related to friction, leading to improved accuracy and repeatability.
Even Loading with Simultaneous Tightening: Multiple fasteners can be loaded simultaneously, ensuring uniform load distribution and precise sealing.
Prevents Galling: Hydraulic tensioning reduces the likelihood of galling issues associated with high torque loads, particularly in challenging environments.
Time Savings: Improved preload accuracy and repeatability lead to reduced installation times and more predictable maintenance schedules.
Conclusion
Bolt tensioning, particularly with hydraulic tensioners, offers numerous advantages over traditional torquing methods in heavy-duty applications, ensuring safety, efficiency, and reliability. In industries like oil & gas and turbomachinery, where precision and performance are paramount, investing in hydraulic tensioning systems can significantly enhance operational outcomes and mitigate risks associated with bolted joint failures.