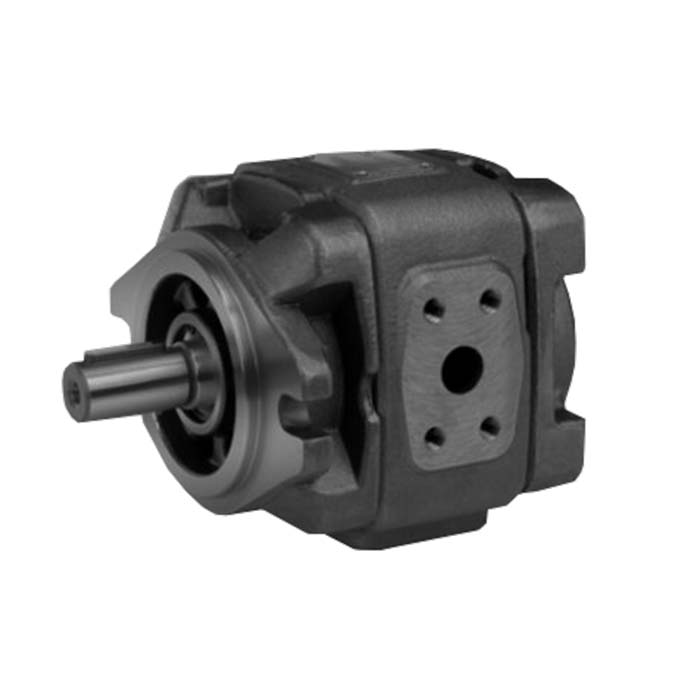
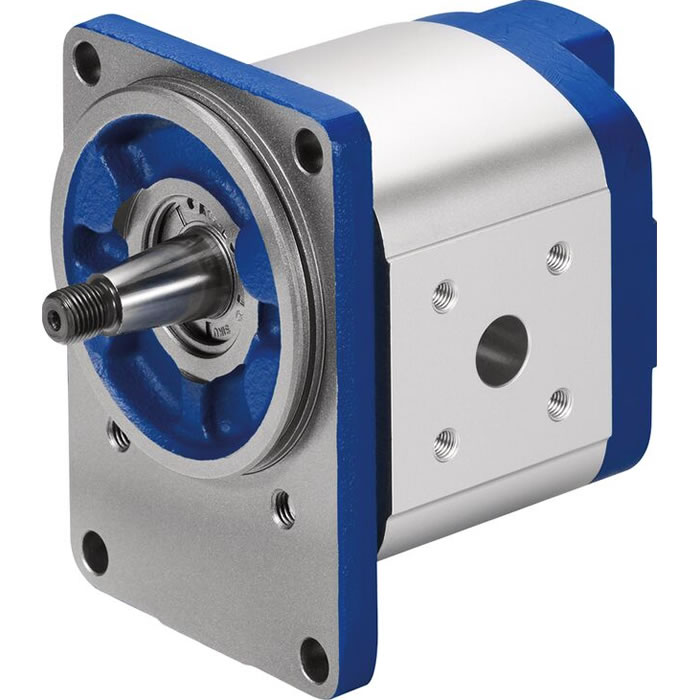
Internal Gear Pumps: A Complete Overview
Introduction:
The internal meshing gear pump is a positive displacement pump that operates based on the principle of meshing gears.
In this article, we will delve into the working principle, design considerations, advantages,
disadvantages, and applications of internal meshing gear pumps.
1. Working Principle of Internal Meshing Gear Pump:
The internal meshing gear pump consists of two gears, namely the driving gear (or the rotor) and the driven gear (or the idler).
These gears are housed within a pump casing with close tolerances.
As the driving gear rotates, it meshes with the driven gear, creating sealed chambers between the gear teeth and the pump casing.
This meshing action effectively traps the fluid, which is then transported from the suction side to the discharge side of the pump.

2. Design of Internal Meshing Gear Pump:
The design of an internal meshing gear pump involves several key considerations:
a. Gear Profile:
The shape and profile of the gear teeth play a crucial role in achieving efficient fluid transfer.
Common gear profiles include spur, helical, herringbone, and double herringbone.
b. Pump Casing:
The pump casing is designed to provide precise tolerances between the gears and the casing,
ensuring minimal leakage and maximum volumetric efficiency.
c. Shaft Sealing:
Various sealing methods, such as mechanical seals or packing glands,
are employed to prevent fluid leakage along the pump shaft.
d. Material Selection:
The choice of materials for gears, pump casing, and other components depends on the fluid characteristics,
operating conditions, and compatibility requirements.
3. Advantages of Internal Meshing Gear Pump:
- Precise Flow Control: Internal meshing gear pumps offer excellent volumetric efficiency and
provide precise flow control, making them suitable for applications requiring accurate dosing or metering.
- Self-Priming Capability: These pumps can self-prime, eliminating the need for external priming mechanisms.
- High Pressure and Temperature Handling: Internal meshing gear pumps are capable of
handling high pressures and temperatures, making them suitable for demanding applications.
- Low Noise and Vibration: Due to their compact design and smooth operation,
internal meshing gear pumps generate minimal noise and vibration.
4. Disadvantages of Internal Meshing Gear Pump:
- Limited Viscosity Range: Internal meshing gear pumps may struggle to handle fluids with high viscosities,
as the tight clearances between gears and casing can lead to increased friction and reduced efficiency.
- Susceptible to Wear: Continuous gear meshing can result in wear over time,
requiring regular maintenance and replacement of worn components.
Limited pressure rating: Internal gear pumps typically have a limited pressure rating, typically around 1500 psi.
Sensitive to contamination: Internal gear pumps are sensitive to contamination, so it is important to use clean fluid.
5. Application of Internal Meshing Gear Pump:
• Alcohols and solvents
• Liquid Terminals
• Lube Oils
• Asphalt Hot Mix
• Soaps and surfactants
• Fuel oil and lube oil
• Paints, pigments, ink
• Polyurethane foam (Isocyanate and polyol)
Conclusion:
Internal meshing gear pumps offer reliable and efficient fluid transfer solutions across various industries.
Their precise flow control, self-priming capability, and ability to handle high pressures and temperatures
make them a preferred choice for many applications. However, their limited viscosity range and susceptibility
to wear should be considered when selecting them for specific operational requirements.