How to calculate hydraulic cylinder force
The Hydraulic Cylinder is an essential component of Hydraulic Systems and plays a pivotal role
in the operation of various machines. It serves as the backbone, enabling the pushing, pulling,
lifting, or dropping actions necessary for these machines to perform their tasks effectively.
Without the design and production of Hydraulic Cylinders, the industrialized world as we know it would not exist.
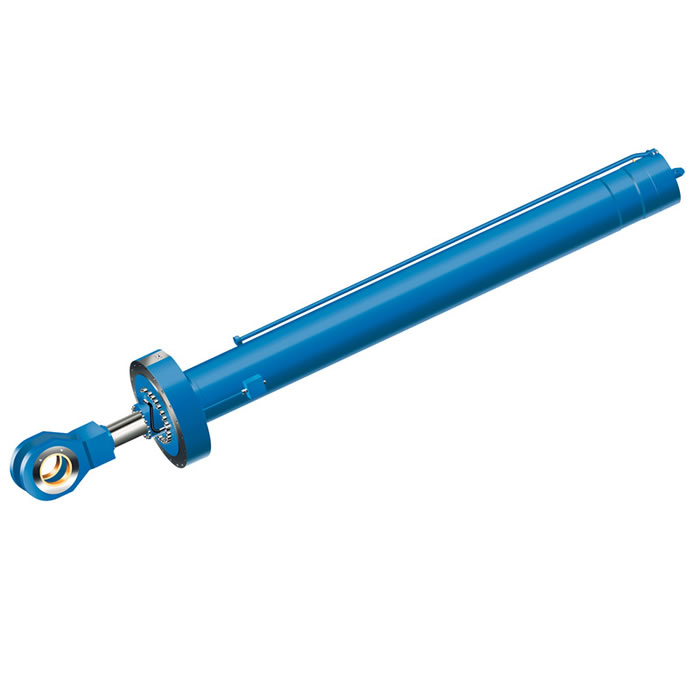
Despite their ability to perform complex tasks, hydraulic cylinders are relatively simple in design.
They consist of a cylindrical barrel or tube that houses a piston and piston rod assembly.
The piston divides the cylinder into two chambers: the pressure (or power) chamber
and the return (or exhaust) chamber. Hydraulic fluid is used to transmit force within these chambers.
The cylinder in a hydraulic system typically consists of five main components:
1. Cylinder Barrel: The cylinder barrel is a cylindrical tube that forms the main body of the cylinder.
It provides the housing for other internal components and serves as a guide for the piston's movement.
The barrel is usually made from high-strength steel or other durable materials to withstand high pressures and loads.
2. Piston: The piston is a cylindrical component that fits inside the cylinder barrel
and divides it into two chambers: the pressure chamber and the return chamber.
It is sealed against the inner walls of the barrel to prevent fluid leakage between these chambers.
The piston receives hydraulic pressure on one side, which creates a force that moves it along with its attached rod.
3. Piston Rod: The piston rod, also known as the ram or plunger, extends from one
end of the piston outside of the cylinder barrel. It transmits force from the moving piston
to an external load or mechanism. The rod is typically made from hardened steel
to withstand bending and twisting forces during operation.
4. Gland or Cylinder Head: The gland, also referred to as the cylinder head, is located at one
end of the cylinder barrel and provides a seal around the piston rod where it exits from the cylinder assembly.
It contains seals or packing materials to prevent fluid leakage between the atmosphere and inside of the cylinder.
5. Seals: Seals are crucial components in hydraulic cylinders as they ensure proper sealing between different
areas within them, preventing fluid leaks and maintaining system integrity. Various types of seals are used
in hydraulic cylinders, including O-rings, wipers, wear rings, backup rings, and more.
These five main components work together to enable controlled movement and force transmission
within hydraulic cylinders, allowing them to perform various tasks in different applications effectively.
Before Calculating Hydraulic Cylinder Force
Before calculating hydraulic cylinder force, it is important to gather the necessary information
and understand the variables involved. Here are some key factors to consider:
1. Cylinder Bore Diameter: The bore diameter refers to the internal diameter of the cylinder barrel.
It is typically measured in millimeters (mm) or inches (in).
This value determines the surface area on which hydraulic pressure acts.
2. Hydraulic Pressure: Hydraulic pressure is the force exerted by the hydraulic
fluid on the piston inside the cylinder. It is usually measured in pounds per square inch (psi), bar, or pascal (Pa).
3. Piston Rod Diameter: The piston rod diameter refers to the diameter of the rod that extends
from one end of the piston outside of the cylinder barrel. It is also measured in millimeters or inches.
4. Frictional Force: Frictional force represents any resistance or friction encountered during movement
within the hydraulic system, such as friction between seals and surfaces or friction caused by load resistance.
5. Load Characteristics: Consideration should be given to factors such as load weight, direction,
and any additional forces acting on it (e.g., gravity).
Once you have gathered this information, you can proceed with calculating hydraulic cylinder force
using appropriate formulas based on these variables. Keep in mind that there may be additional factors
specific to your application that need to be considered for accurate calculations.
Hydraulic Cylinder Force Calculation Formula
The formula for calculating the force exerted by a hydraulic cylinder is:
Force = Pressure × Area
Where:
- Force is the resulting force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder, measured in units of force (such as pounds or newtons).
- Pressure is the hydraulic pressure acting on the piston, measured in units of pressure (such as psi or pascals).
- Area is the cross-sectional area of the piston, measured in square units (such as square inches or square millimeters).
To calculate the area of the piston, you can use the formula:
Area = π × (Radius)^2
Where:
- π (Pi) is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14159.
- Radius refers to half of the diameter of the piston.
By substituting this area formula into the force calculation formula,
you can determine the force exerted by a hydraulic cylinder based on its pressure and piston dimensions.