How to Distinguish Between Different Types of Hydraulic Valves?
How to Distinguish Between Different Types of Hydraulic valves?
Which Hydraulic Valve is Right for Your Application?
Hydraulic Valve Classification: A Complete Guide for Engineers
Choosing the Right Hydraulic Valve: A Procurement Guide
Understanding Hydraulic Valves: Types, Functions, and applications
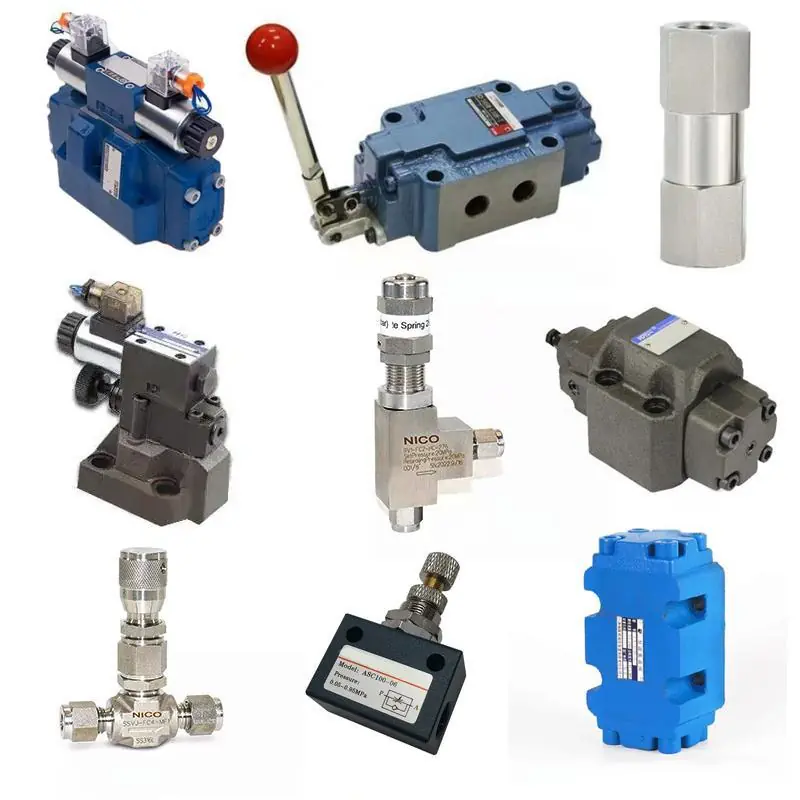

The above mentioned questions can be solved in the following article, please read carefully:
A Comprehensive Guide to Hydraulic Valve Classification
Hydraulic valves are crucial components in Hydraulic Systems, controlling the flow, pressure, and direction of hydraulic fluid.
Understanding the various classifications of these valves is essential for proper system design and selection.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of different ways to categorize hydraulic valves.
1. Classification by Function:
This is perhaps the most common and practical classification method. It categorizes valves based on their primary function within the hydraulic system:
- Pressure Control Valves: These valves regulate fluid pressure. Examples include:
- Overflow valves: Limit maximum system pressure.
- Pressure Reducing Valves: Reduce incoming pressure to a desired level.
- Sequence Valves: Control the order of operation of different Hydraulic Cylinders or motors.
- Flow Control Valves: These valves regulate the flow rate of hydraulic fluid. Examples include:
- Throttle Valves: Control flow by restricting the passage of fluid.
- Speed Regulating Valves: Control the speed of hydraulic actuators.
- Directional Control Valves: These valves control the direction of fluid flow. Examples include:
- Check Valves: Allow fluid to flow in only one direction.
- Solenoid Valves: Electrically controlled valves that direct fluid flow.
- Reversing Valves: Change the direction of fluid flow to reverse the motion of an actuator.
2. Classification by Structure:
This method categorizes valves based on their internal construction:
- Slide Valves: Utilize a sliding element (e.g., spool) to control fluid flow.
- Seat Valves: Employ a sealing element (e.g., ball, cone) that sits on a seat to control flow.
- Jet Valves: Utilize a jet of fluid to control flow.
3. Classification by Operation Method:
This method categorizes valves based on how they are actuated:
- Manual Valves: Operated manually using handles, levers, or pedals.
- Motorized Valves: Operated by external forces such as springs, Hydraulic Cylinders, or pneumatic actuators.
- Electric Valves: Operated by electrical signals, such as solenoid valves or servo valves.
4. Classification by Connection Method:
This method categorizes valves based on how they are connected to the hydraulic system:
- Pipe Connection: Valves with threaded or flanged connections for direct attachment to pipes.
- Plate and Stacking Connection: Valves mounted on plates that can be stacked together to create complex valve banks.
- Cartridge Connection: Valves inserted into cartridge housings, offering flexibility in system design.
5. Classification by Control Method:
This method categorizes valves based on the sophistication of their control:
- Electro-hydraulic Proportional Valves: Utilize electrical signals to proportionally control fluid flow or pressure.
- Servo Valves: High-performance valves with precise control characteristics, often used in high-accuracy applications.
- Digital Control Valves: Utilize digital signals for precise and flexible control of valve operation.
6. Other Classification Methods:
- Switch or Fixed Value Control Valves: These valves have fixed or limited adjustments to their operating characteristics.
- Classification by Primary Function: This method further categorizes valves into pressure control valves, flow control valves, and directional control valves.
Conclusion:
Understanding these different classifications is crucial for selecting the appropriate valves for a specific hydraulic system.
By carefully considering the application requirements and available valve options, engineers can design and implement efficient and reliable hydraulic systems.