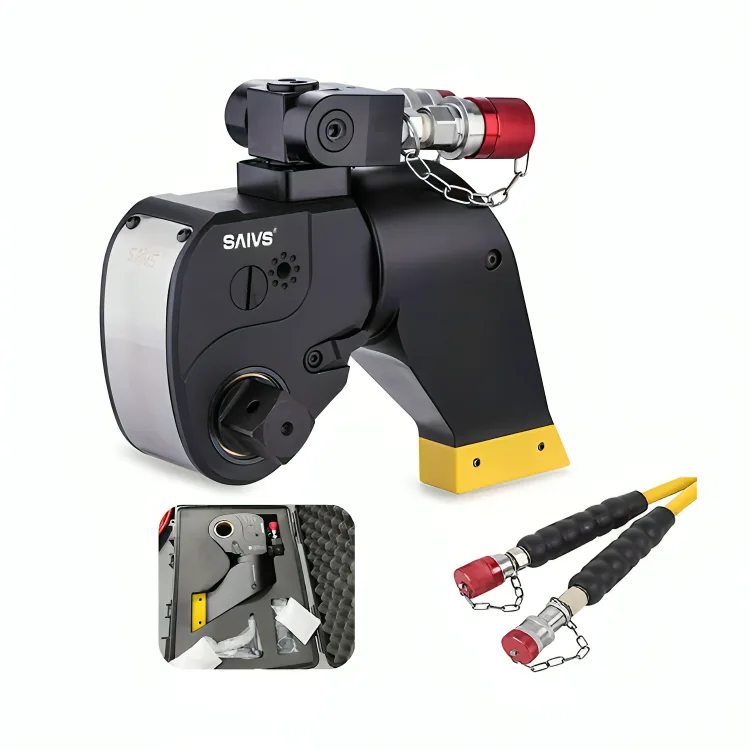
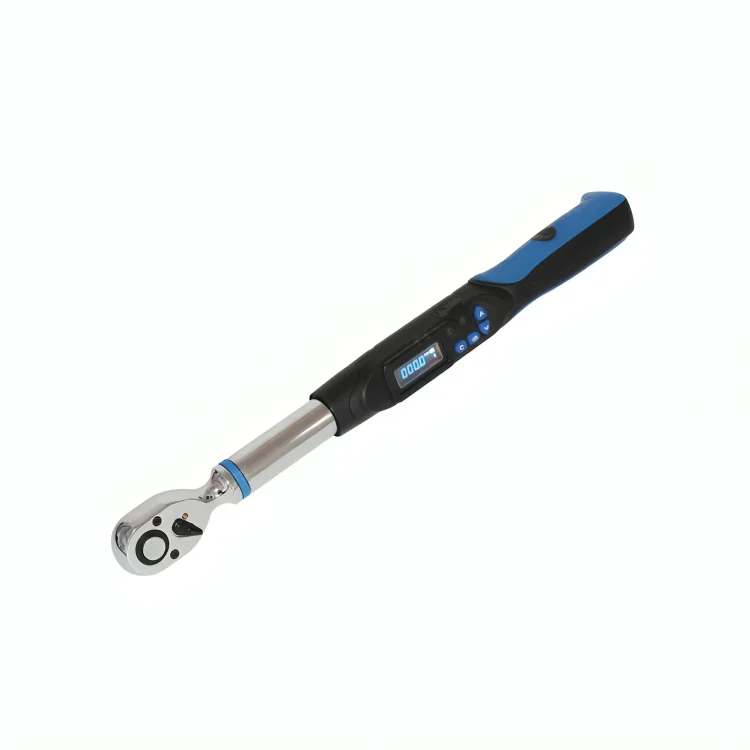
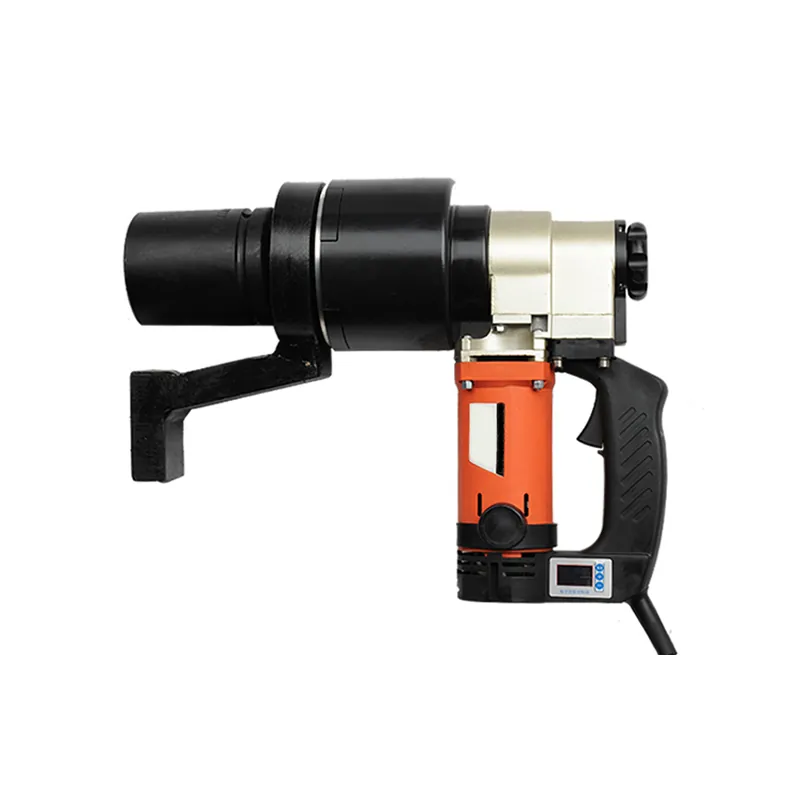
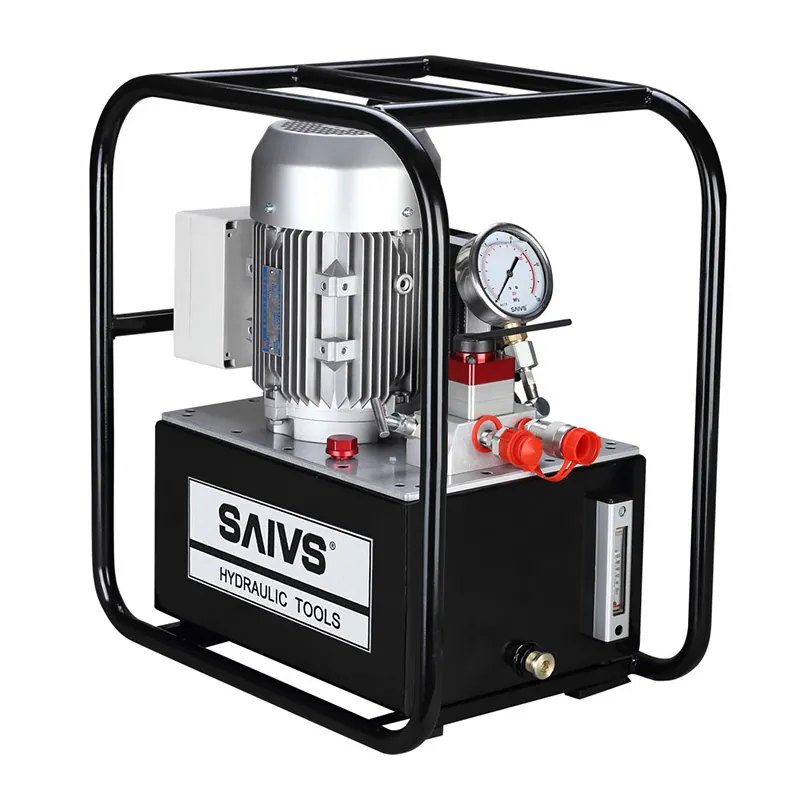
The importance of setting the right torque
Setting the right torque when tightening fasteners is of utmost importance for several reasons.
1. Safety: Properly tightened fasteners ensure the safe and reliable operation of equipment,
machinery, and structures. Under-tightened fasteners can lead to loosening over time, increasing
the risk of accidents, failures, or disassembly. Over-tightened fasteners can cause stress
concentration and potential failure points, compromising structural integrity.
2. Performance: Fasteners play a crucial role in maintaining the performance of mechanical systems.
Setting the correct torque ensures that components are securely held together,
minimizing vibrations, reducing wear and tear, and optimizing overall system performance.
3. Preventing damage: Fasteners that are either under-tightened or over-tightened can cause
damage to both the fastener itself and the mating parts they connect. Under-tightening may
result in excessive movement or slippage between components, leading to premature wear or failure.
Over-tightening can cause thread stripping or deformation, leading to irreversible damage.
4. Uniformity: Using consistent torque settings ensures uniform clamping force across multiple
fasteners within a system or assembly. This helps distribute loads
evenly and minimizes stress concentrations on specific components.
5. Specifications compliance: Manufacturers provide torque specifications for specific
applications based on engineering calculations and testing to ensure optimal performance
and safety standards are met. Following these specifications
guarantees that equipment is assembled according to design requirements.
6. Warranty requirements: In many cases, warranty coverage may be contingent upon adhering
to specified torque values during installation or maintenance procedures.
Failure to follow these guidelines could void warranties provided by manufacturers.
To achieve accurate torque application
a) Use calibrated tools: Regular calibration ensures that
torque wrenches are accurate within specified tolerances.
b) Follow manufacturer guidelines: Consult product manuals
for recommended torque values specific to each application.
c) Consider factors affecting torque values: Account for variables such as lubrication conditions,
material properties (e.g., hardness), thread conditions
(cleanliness), environmental factors (temperature), etc.
d) Proper technique: Apply force smoothly without sudden jerks or impacts;
maintain alignment with the fastener axis; avoid using extensions unless recommended by manufacturers.
e) Verify results if necessary: For critical applications or where accuracy is paramount,
consider using additional verification methods like angle measurement techniques alongside torquing.