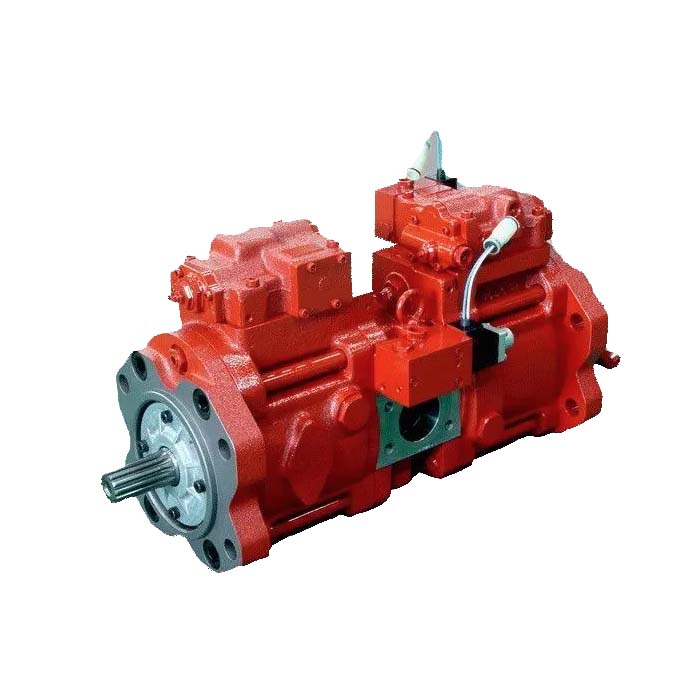
Unleashing Hydraulic Pump Benefits: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
Did you know Hydraulic pumps play a crucial role in various industries, from construction to agriculture?
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of hydraulic pumps, exploring their functions, components, types, and applications.
Understanding Hydraulic Pumps
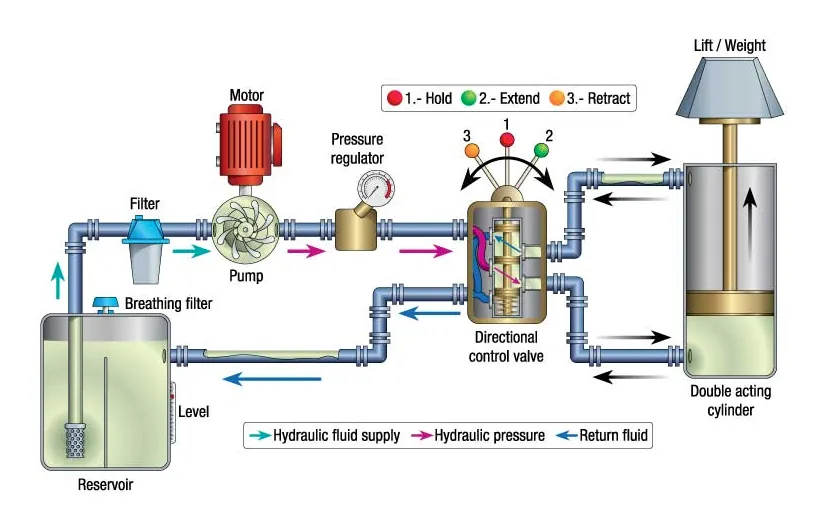
Working Principle of Hydraulic Pumps
Hydraulic pumps operate based on the principle of converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy.
They create fluid flow and generate hydraulic pressure, enabling the transmission of force and motion within the system.
Common types of hydraulic pumps include gear pumps, Vane Pumps, and piston pumps.
Each type utilizes different mechanisms to achieve fluid displacement and pressure generation.
Types and Applications of Hydraulic Pumps
Piston Pumps
Piston pumps are high-pressure pumps that are more complex and have a higher initial cost compared to gear pumps.
They are commonly used in truck-mounted cranes and snow and ice control systems.
Piston pumps operate by utilizing a cylinder block with pistons that extract oil
from the supply port and pressurize it before directing it through the outlet.
Gear Pumps
Gear pumps are renowned for their simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and versatility.
They are commonly used in truck-mounted Hydraulic Systems and find applications in various industries.
The working principle of gear pumps involves trapping oil in the spaces between the teeth of two
gears and the pump's body. As the gears rotate, they transport the oil around the gear cavity
and expel it through the outlet port using centrifugal force.
Vane Pumps
Vane pumps utilize vanes mounted on a rotor to generate hydraulic pressure.
While they were once popular in utility vehicles, they have become less common due to the increased prevalence of gear pumps.
Vane pumps offer improved volumetric power efficiency and reduced noise compared to gear pumps.
Air hydraulic pumps utilize compressed air to generate energy from hydraulic fluids.
They are often used for lifting heavy loads and material transportation. When air pressure is applied,
the pumps engage a piston, compressing the Hydraulic Cylinder and creating a pumping action.
The primary components of air hydraulic pumps include a reservoir,
a pump housing a hydraulic cylinder, a piston system, valves, and a cylinder.
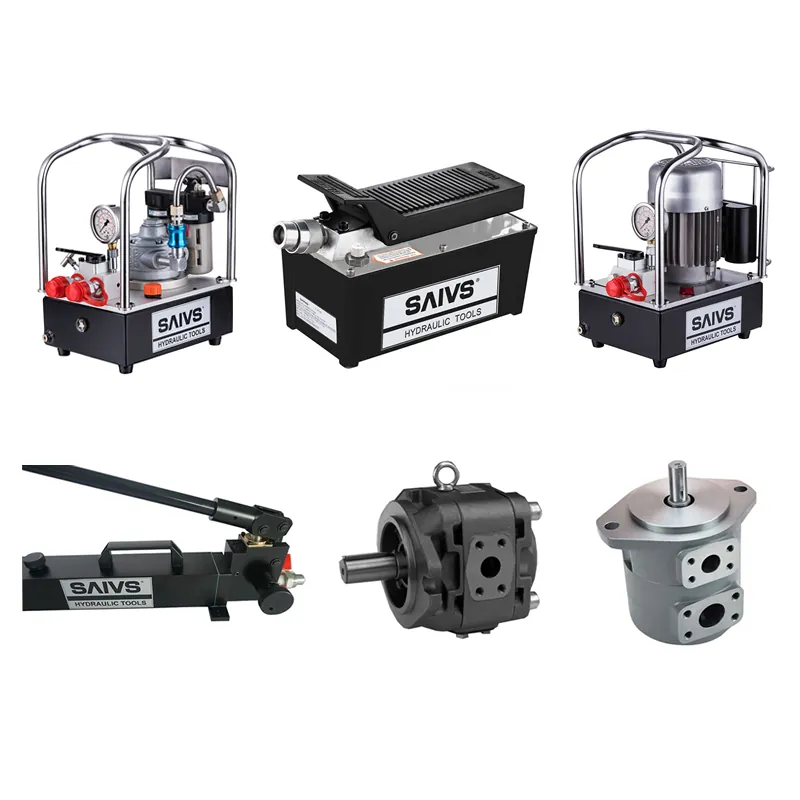
Hydraulic Hand Pumps
Hydraulic hand pumps are manually operated pumps commonly used for hydraulic tools and presses.
They work by creating suction and drawing oil into the cylinder when the pump lever is pressed downwards.
This pumping action allows the oil to be pulled up through the mechanism, providing hydraulic power.
Hand pumps are versatile, reliable, and cost-effective. They are easy to install and maintain,
making them suitable for a wide range of applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
They are particularly useful in remote locations where electricity is not available.
Electric hydraulic pumps rely on electricity to transfer hydraulic fluid to actuators,
playing a critical role in various machinery. These pumps use an electric motor to drive a hydraulic pump,
which then delivers fluid pressure to cylinders, actuators, and Hydraulic Motors.
Electric hydraulic pumps are widely used in automotive, industrial, and agricultural machinery,
as well as in construction, mining, and other heavy-duty applications.
They offer efficient and reliable hydraulic power for a wide range of operations.
Maintenance of Hydraulic Pumps
1. Regular Inspections
Perform visual inspections to check for leaks, damaged components, or signs of wear.
Inspect fittings, seals, and connections for tightness and integrity.
Look for any unusual noises or vibrations during operation.
2. Fluid Level and Condition
Check the hydraulic fluid level regularly and ensure it is within the recommended range.
Monitor the fluid condition, including color, clarity, and presence of contaminants.
If necessary, perform fluid analysis to assess its quality and determine if it requires replacement or filtration.
3. Filter Maintenance
Clean or replace hydraulic filters based on manufacturer recommendations.
Ensure filters are properly installed and functioning effectively to prevent contamination of the hydraulic system.
Regularly monitor filter differential pressure and replace filters when pressure exceeds the recommended limit.
4. Lubrication
Ensure lubrication points, such as bearings and gears, are properly lubricated according to manufacturer guidelines.
Use the recommended lubricants to maintain optimal pump performance and prevent premature wear.
Troubleshooting Hydraulic Pumps
1. Identify Symptoms
Observe and identify any symptoms or abnormal behavior exhibited by the hydraulic pump,
such as unusual noise, low pressure, or erratic operation.
Gather information about the specific symptoms and any recent changes or incidents that may have occurred.
2. Check Fluid Levels
Ensure that the hydraulic fluid level is within the recommended range.
Inspect for any leaks or signs of fluid loss that may indicate a problem in the hydraulic system.
3. Inspect Filters and Strainers
Check hydraulic filters and strainers for clogs or excessive dirt accumulation.
Clean or replace filters as necessary to maintain proper fluid flow and prevent contamination.
4. Examine Connections and Fittings
Inspect hydraulic connections, fittings, and seals for leaks or loose connections.
Tighten or replace any damaged or faulty components.
How to choose a hydraulic pump
SAIVS can provide you with various types of hydraulic pumps to meet your different work needs.
We would manufacture (hydraulic pump) following your specific requirements
We are looking forward to your email and establishing cooperative relationships with you!











